-
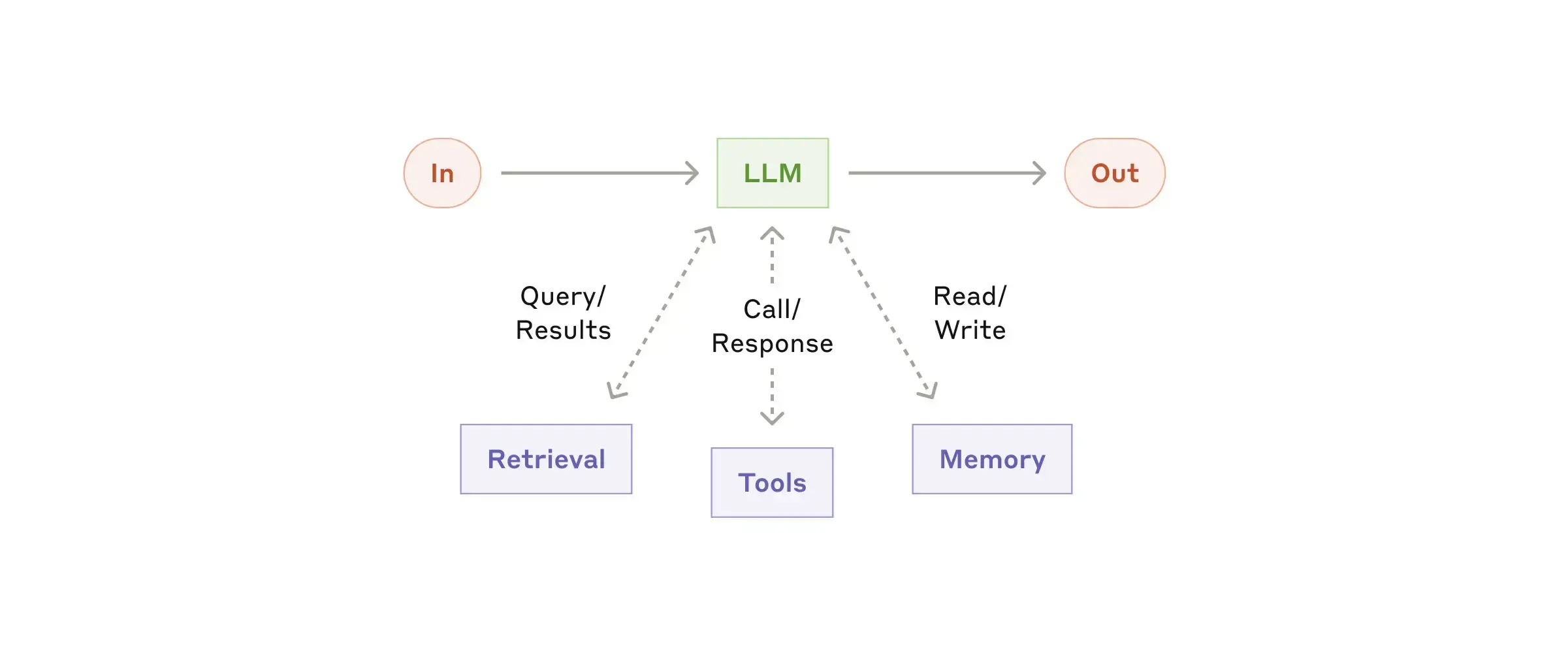
Building block: The augmented LLM
Agentic systems are built upon LLMs enhanced with retrieval, tools, and memory. These models can independently search, select tools, and retain information.
-
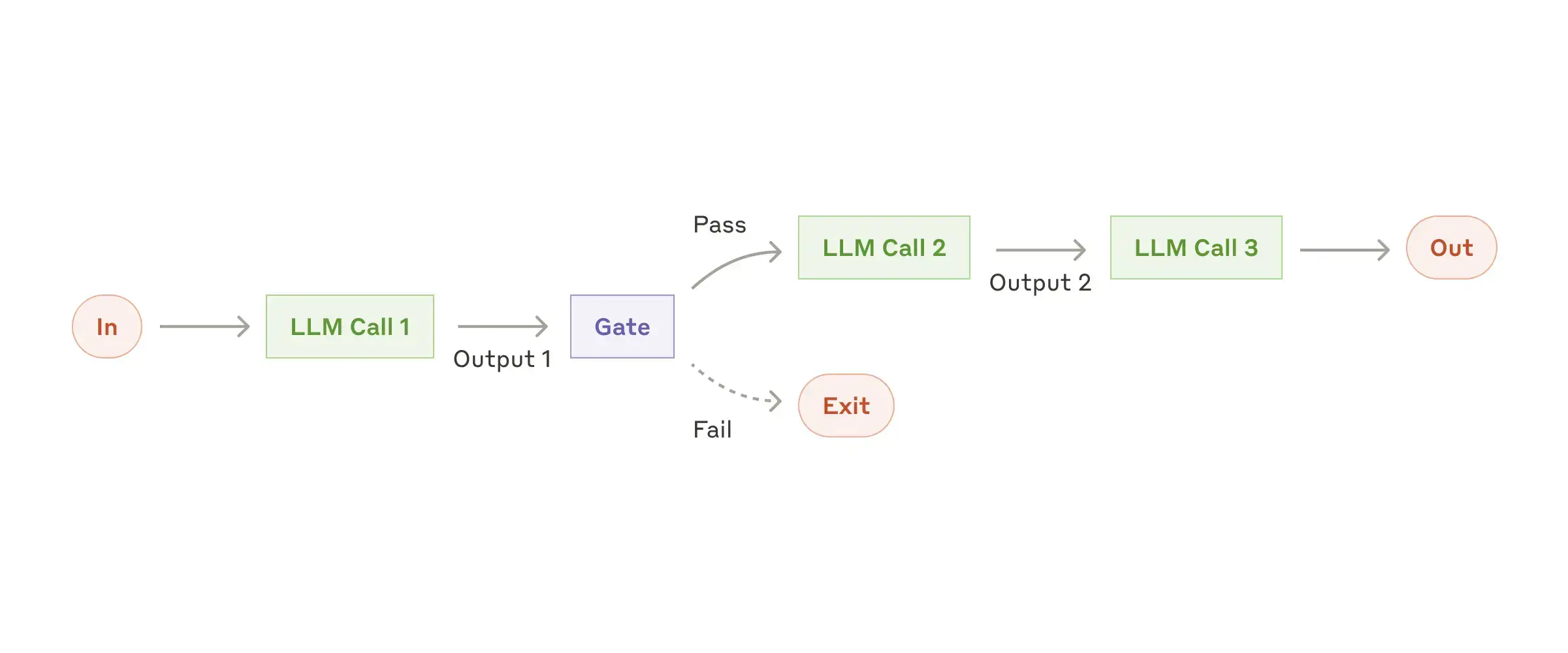
Workflow: Prompt chaining
Prompt chaining decomposes a task into a sequence of steps, where each LLM call processes the output of the previous one
-
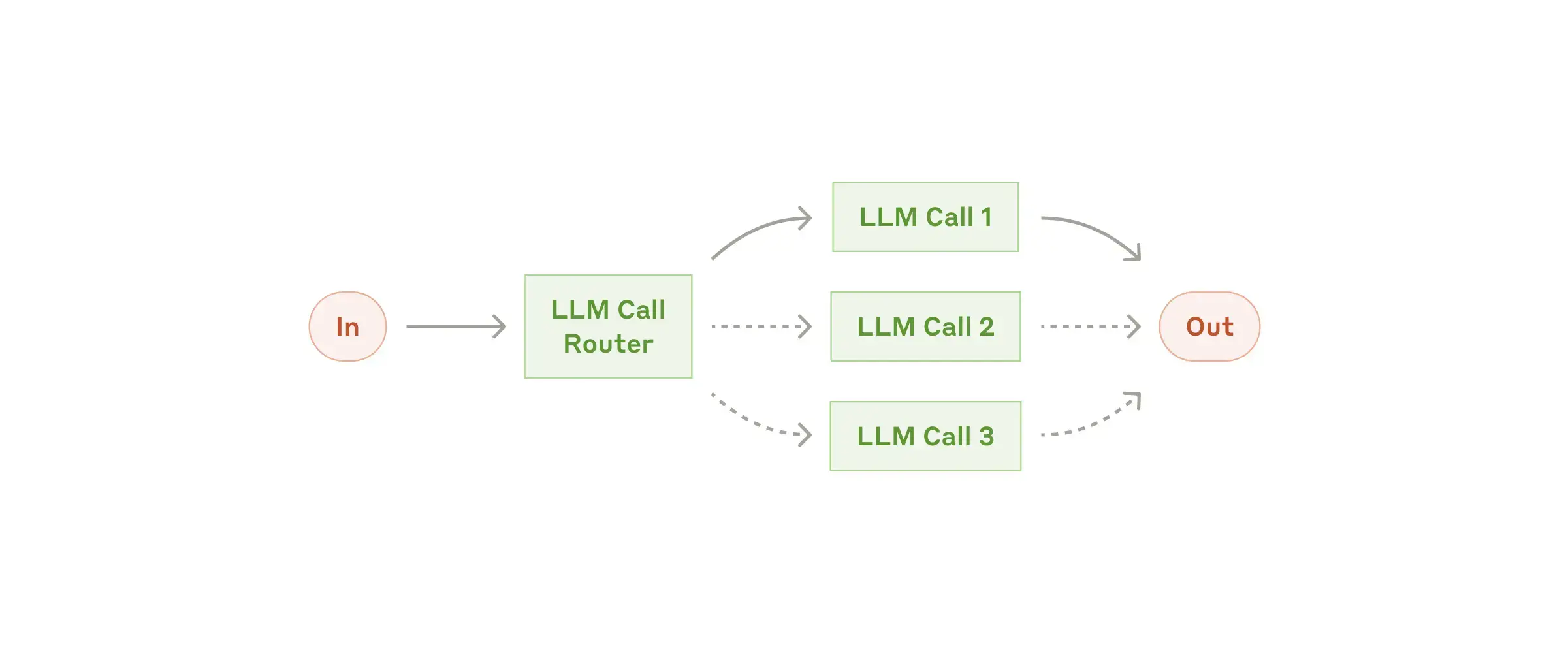
Workflow: Routing
Routing classifies an input and directs it to a specialized followup task.
-
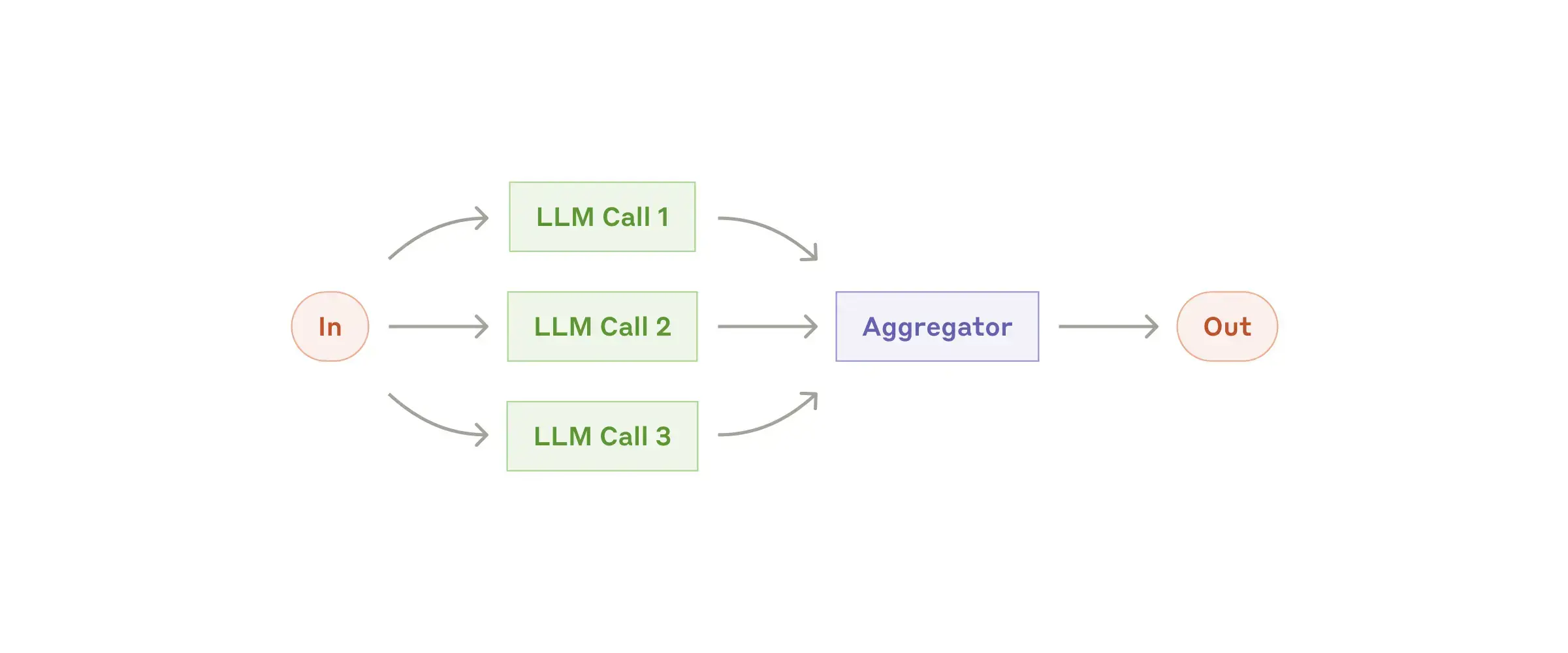
Workflow: Parallelization
LLMs can work simultaneously on a task and have their outputs aggregated programmatically
- Sectioning: Breaking a task into independent subtasks run in parallel.
- Voting: Running the same task multiple times to get diverse outputs.
-
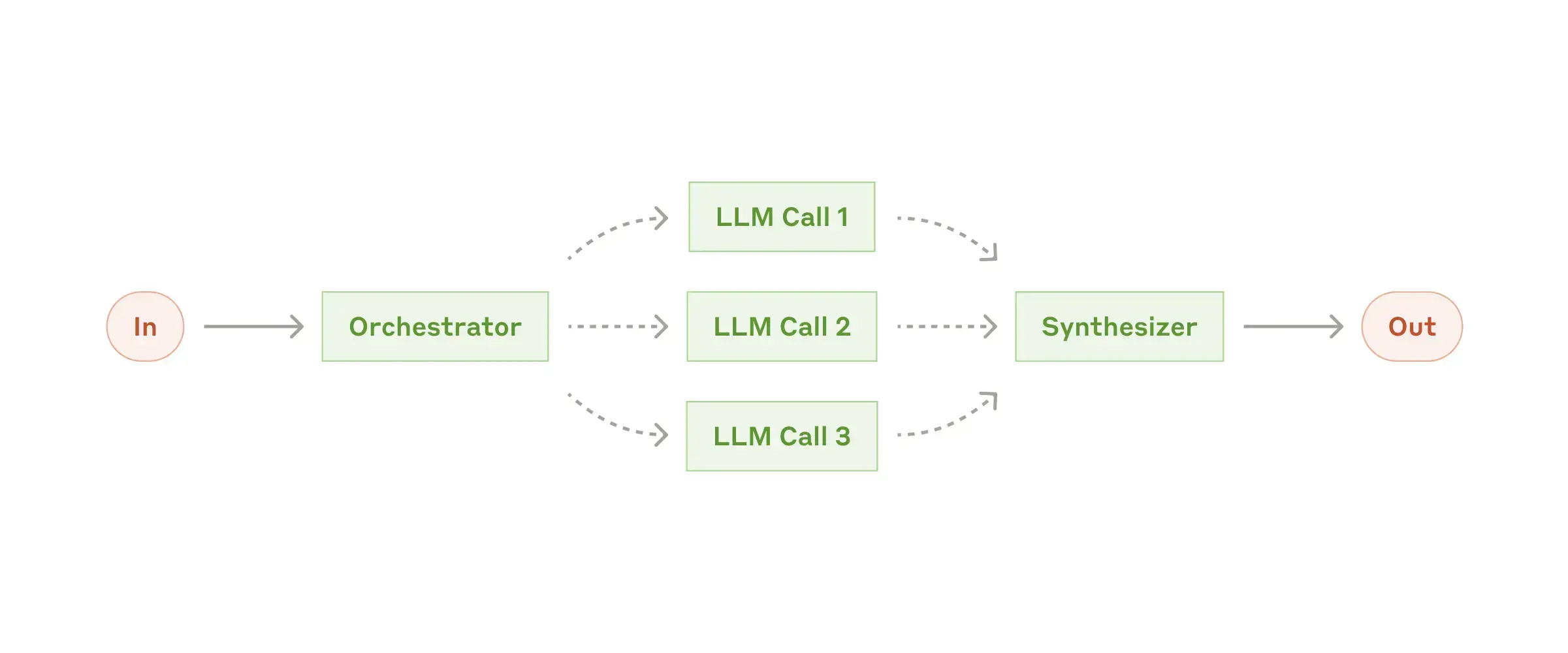
Workflow: Orchestrator-workers
A central LLM dynamically breaks down tasks, delegates them to worker LLMs, and synthesizes their results.
-
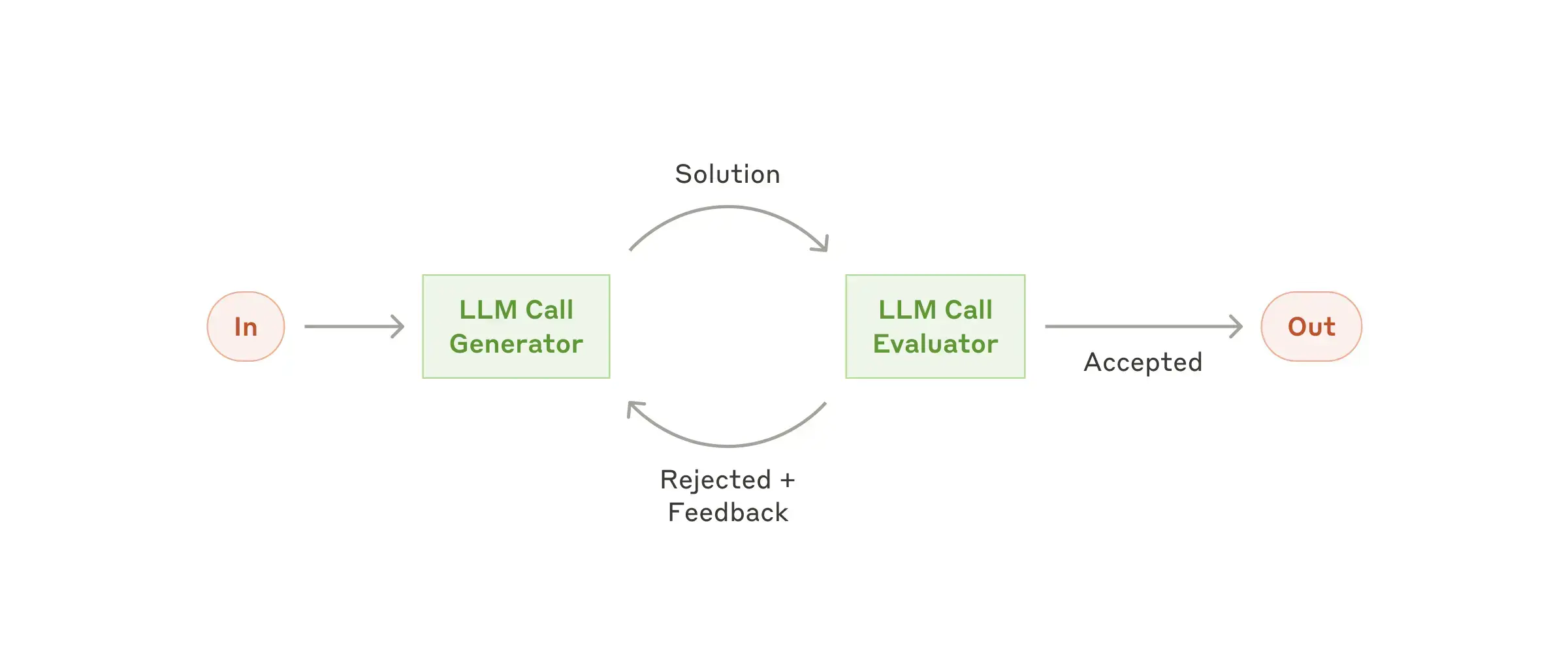
Workflow: Evaluator-optimizer
one LLM call generates a response while another provides evaluation and feedback in a loop.
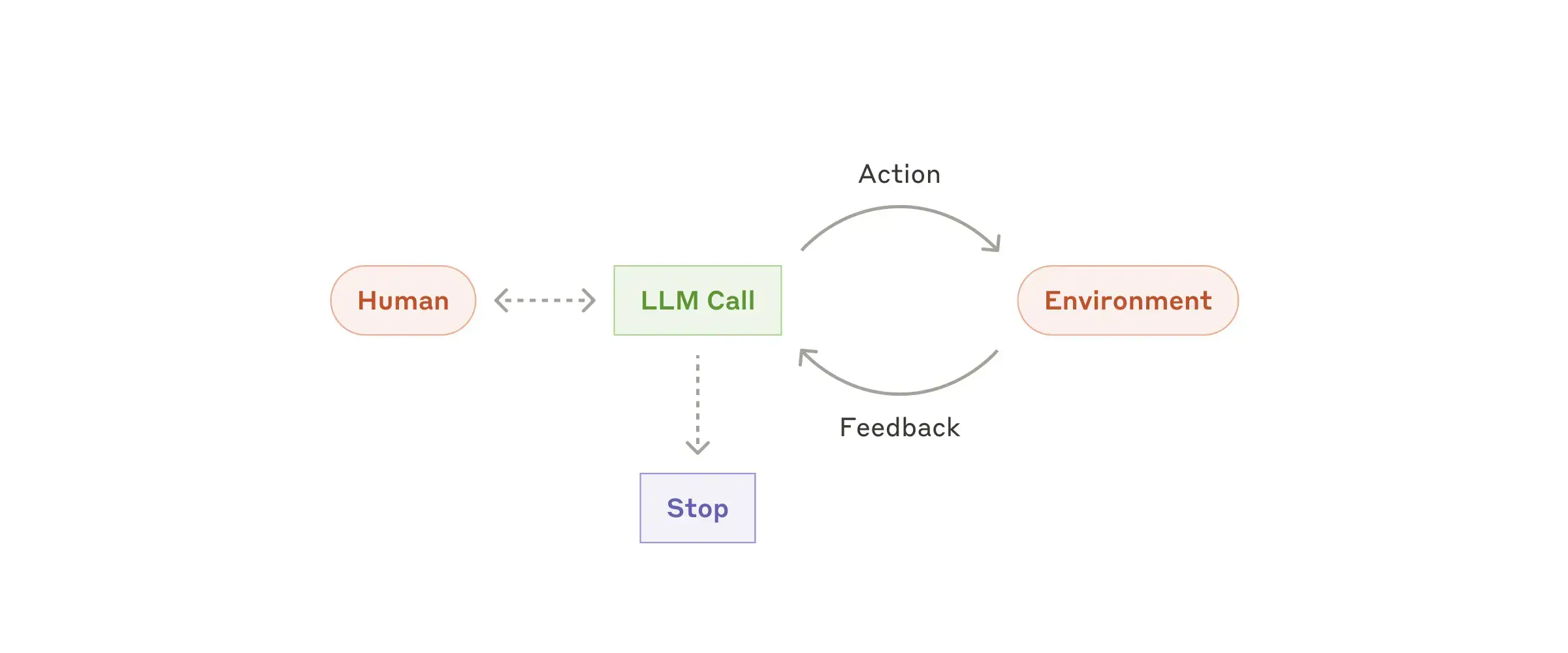
Agents
LLM agents autonomously execute tasks, leveraging advanced capabilities like reasoning and tool use. They operate independently, gathering real-world data and seeking human input when necessary.
Agents can be used for open-ended problems where it’s difficult or impossible to predict the required number of steps, and where you can’t hardcode a fixed path.
You should consider adding complexity only when it demonstrably improves outcomes.
Reference
https://www.anthropic.com/research/building-effective-agents